Färgprecision med NCS systemet
Kort intro
NCS systemet
Ett logiskt färgsystem
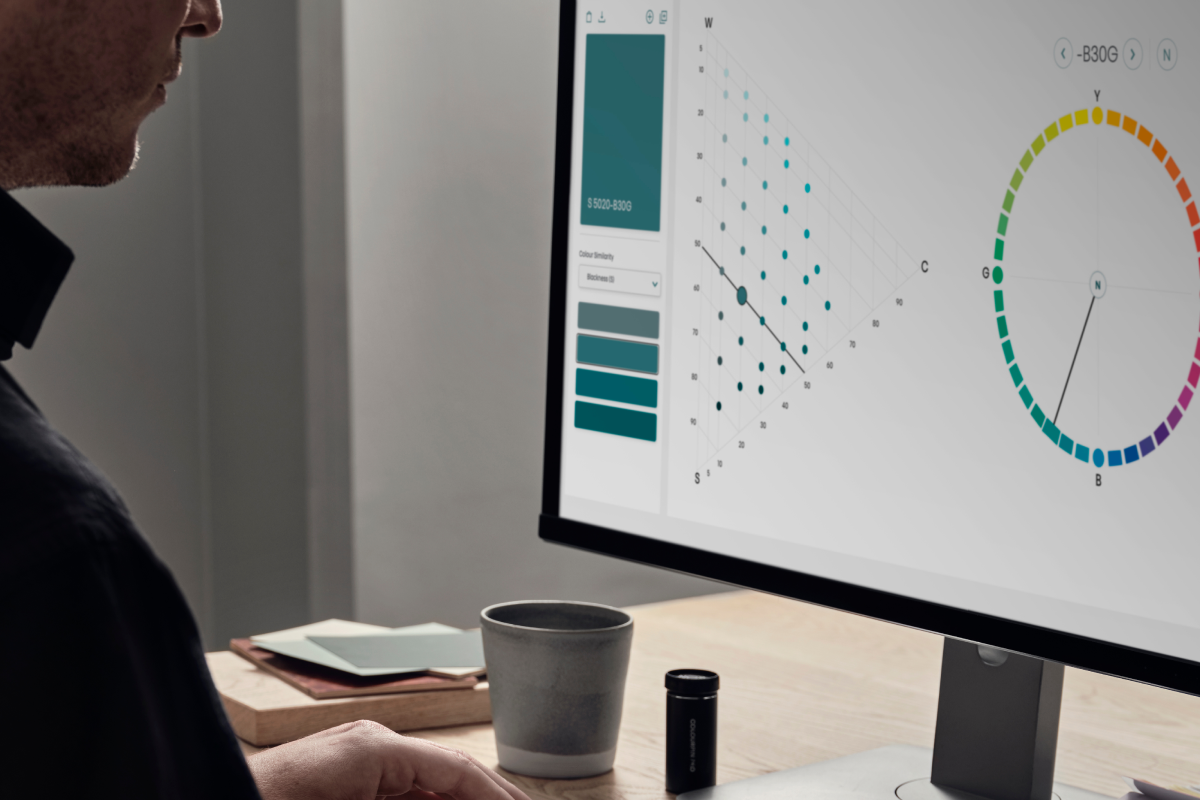

NCS+
Få tillgång till NCS systemet digitalt
Utforska hela NCS systemet och lita på dess logik genom hela din kreativa resa.
Använda NCS systemet
Skapa harmoniserande färgkombinationer
NCS systemet gör det möjligt för dig att validera och förfina dina färgval. Översätt din inspiration till fungerande färgpaletter och lär dig hur du använder NCS systemet i ditt arbete nedan.
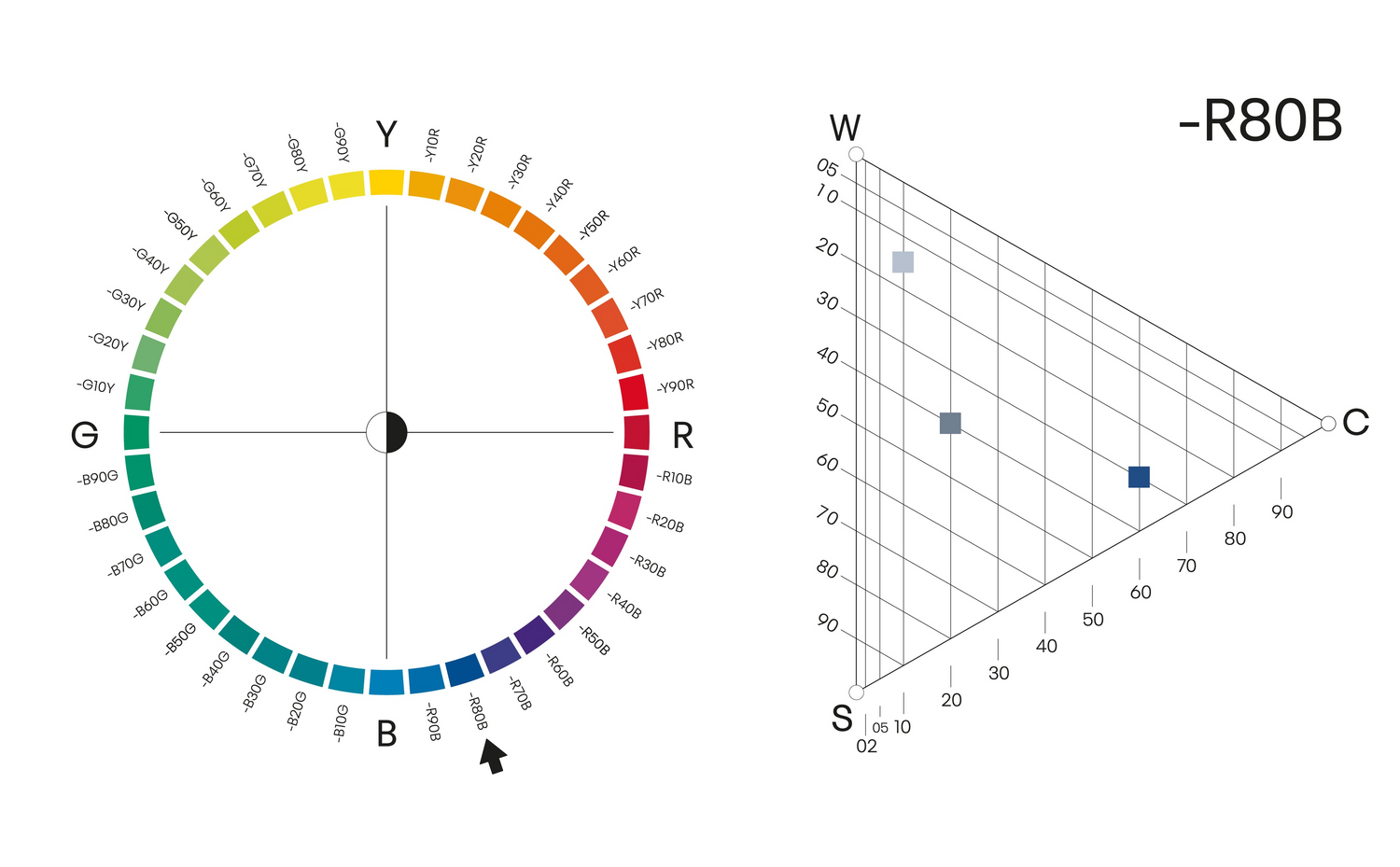
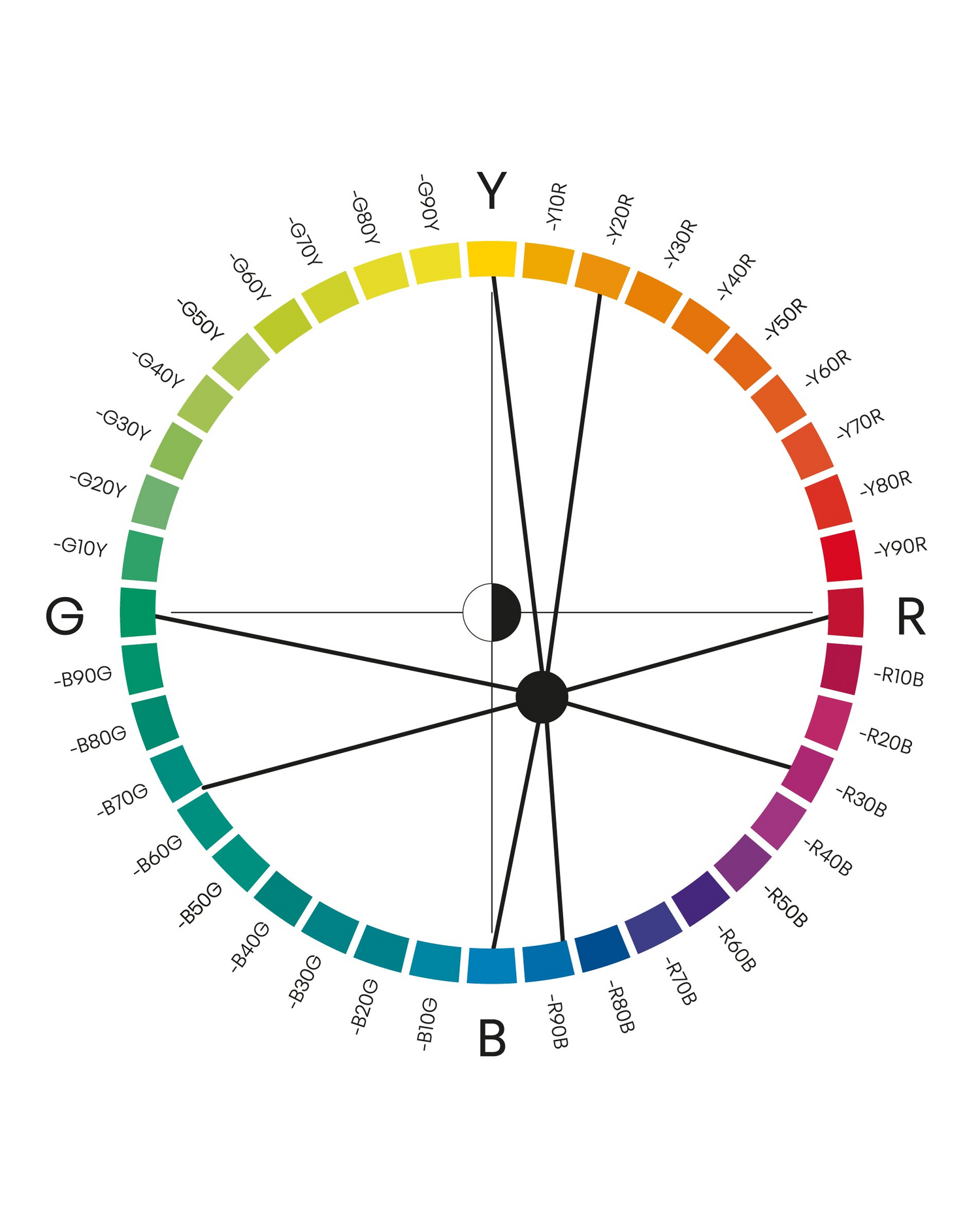
Kulörton
Färger med samma kultörton tillhör samma färgfamilj. Färger med samma kulörton finns på samma plats i cirkeln, till exempel alla nyanser av R80B. Dessa färger finns alla på samma triangel och sida i NCS Atlas 2050. Kulörton är ett vanligt sätt att kombinera färger i inredningsdesign.
KULÖRTON - R80B
Här illustrerat med 3 olika nyanser av kulörtonen R80B.
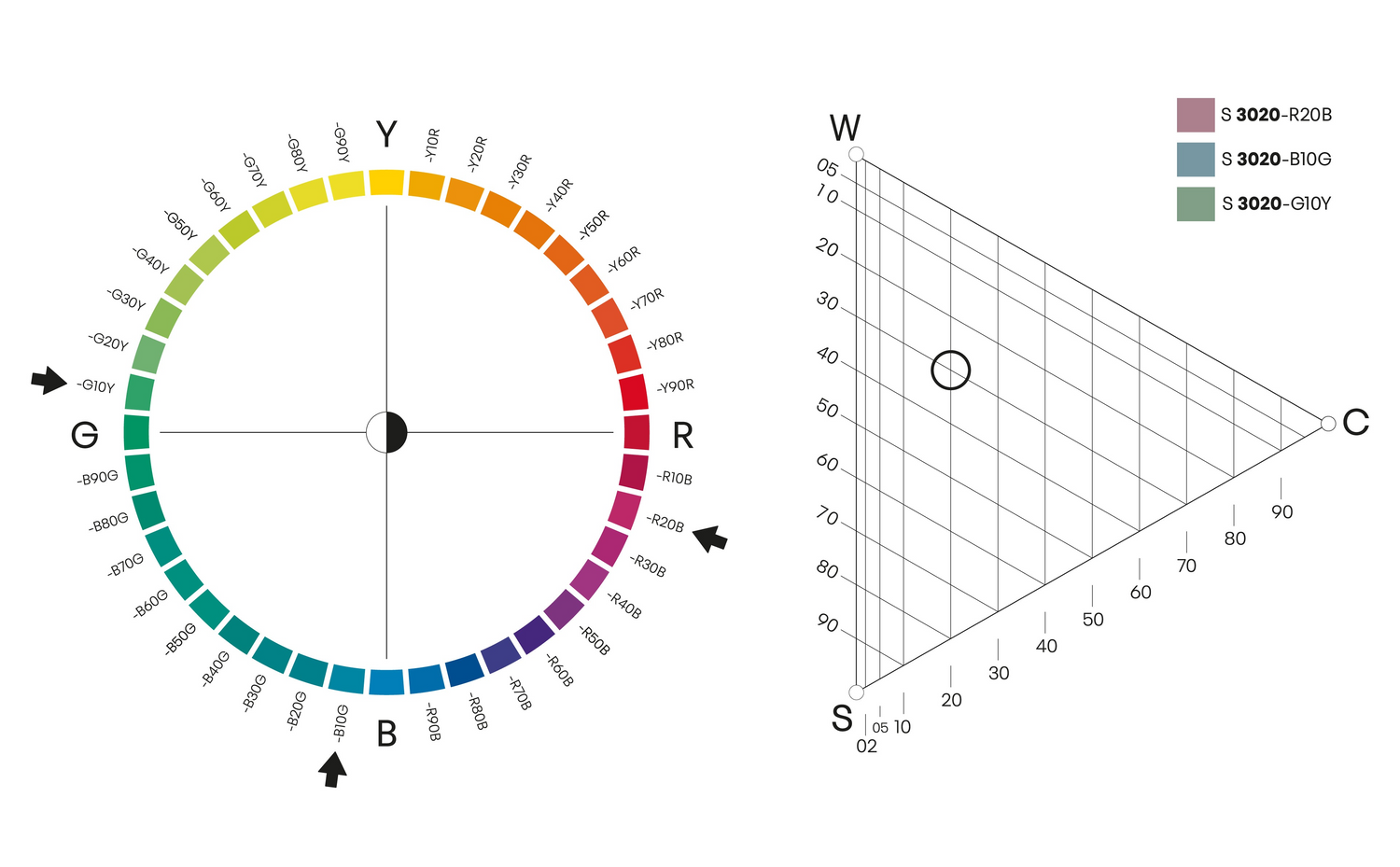
Nyans
Färgprover med samma nyans har samma position i färgtriangeln oavsett kulörton, men finns på olika sidor i NCS Atlas. Nyans är användbart när man väljer färger för ett färgsortiment eller inredning.
NYANS 3020
Här illustrerat med 3 olika kulörtoner av samma nyans 3020.
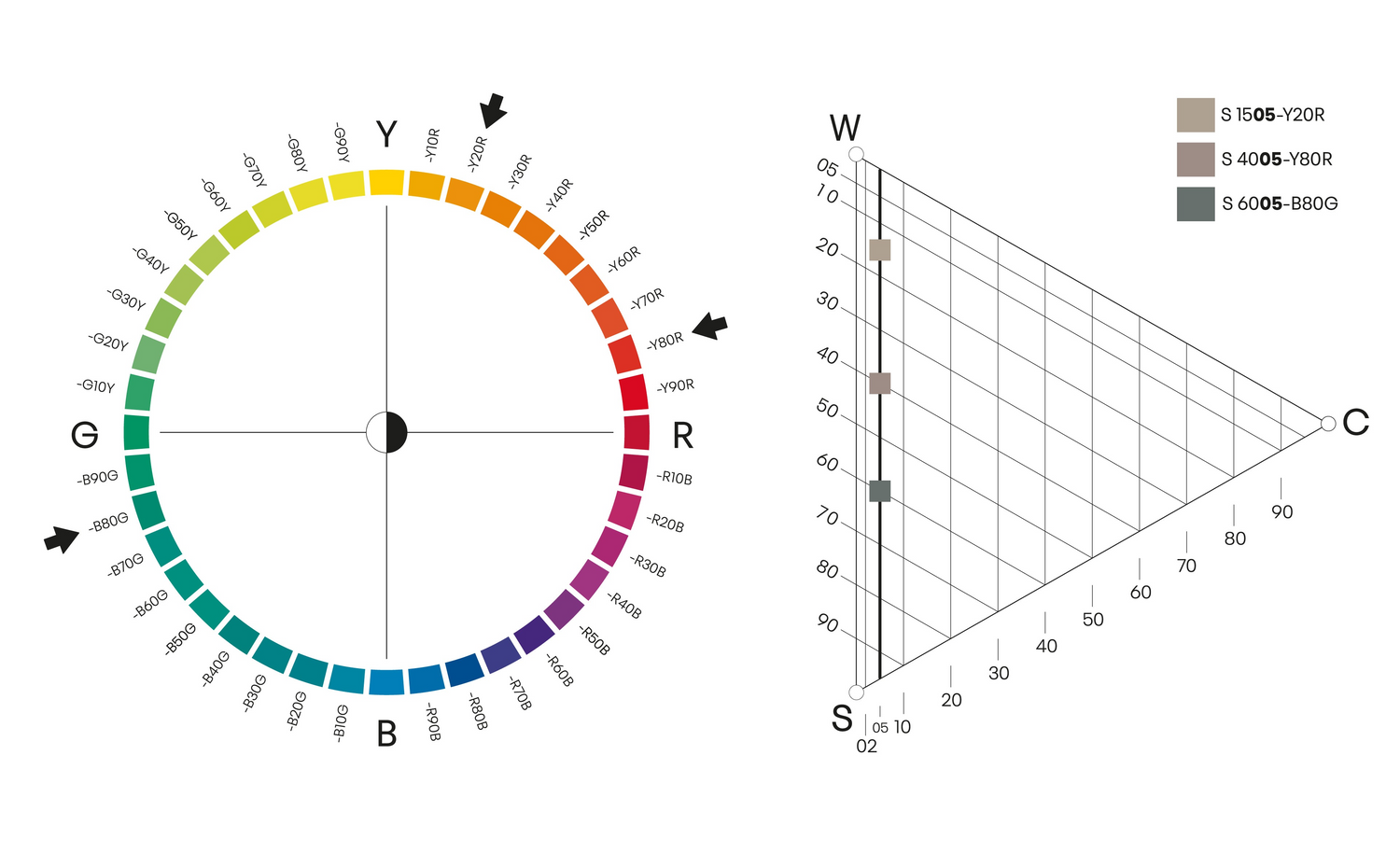
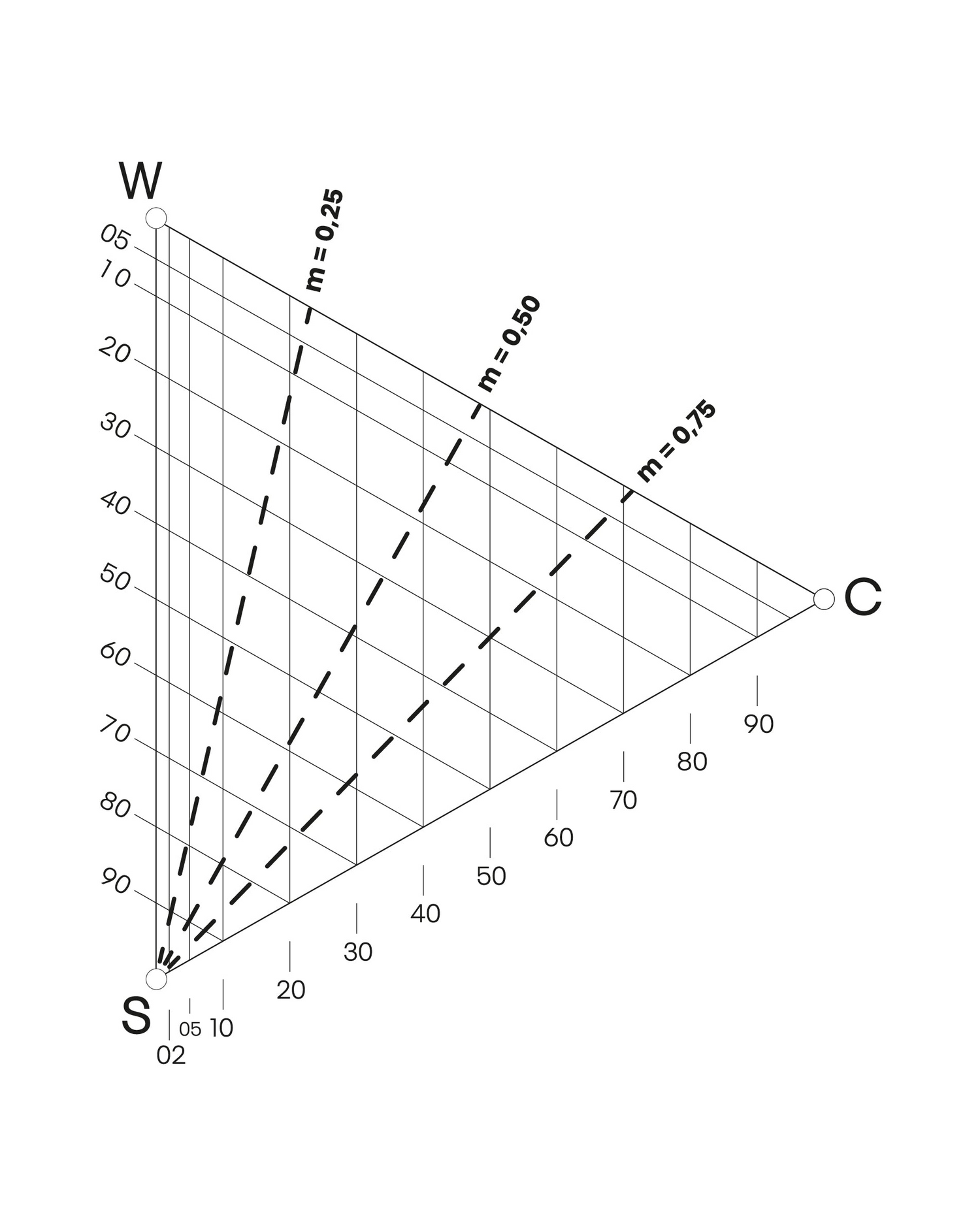
Kromatiskhet
Färgprover som har samma kromatiskhet finns på en rak linje parallellt med gråskalan mellan vitt (W) och svart (S). Ju mindre kromatisk en färg är, desto närmare ligger den gråskalan. Kromatiskhet är användbart inom inredningsdesign och mönsterskapande.
KROMATISKHET XX05
Här är det illustrerat med tre olika färger med samma kromatiskhet (05).
Svarthet
Färgprover som har samma svarthet finns på en rak linje parallellt med skalan mellan vitt (W) och den maximala färgen (C). Ju mindre svartaktig färgen är, desto närmare ligger den denna skala. Svarthet är också användbart inom inredningsdesign.
SVARTHET 20XX
Här är det illustrerat med tre olika färger med samma svarthet (30).
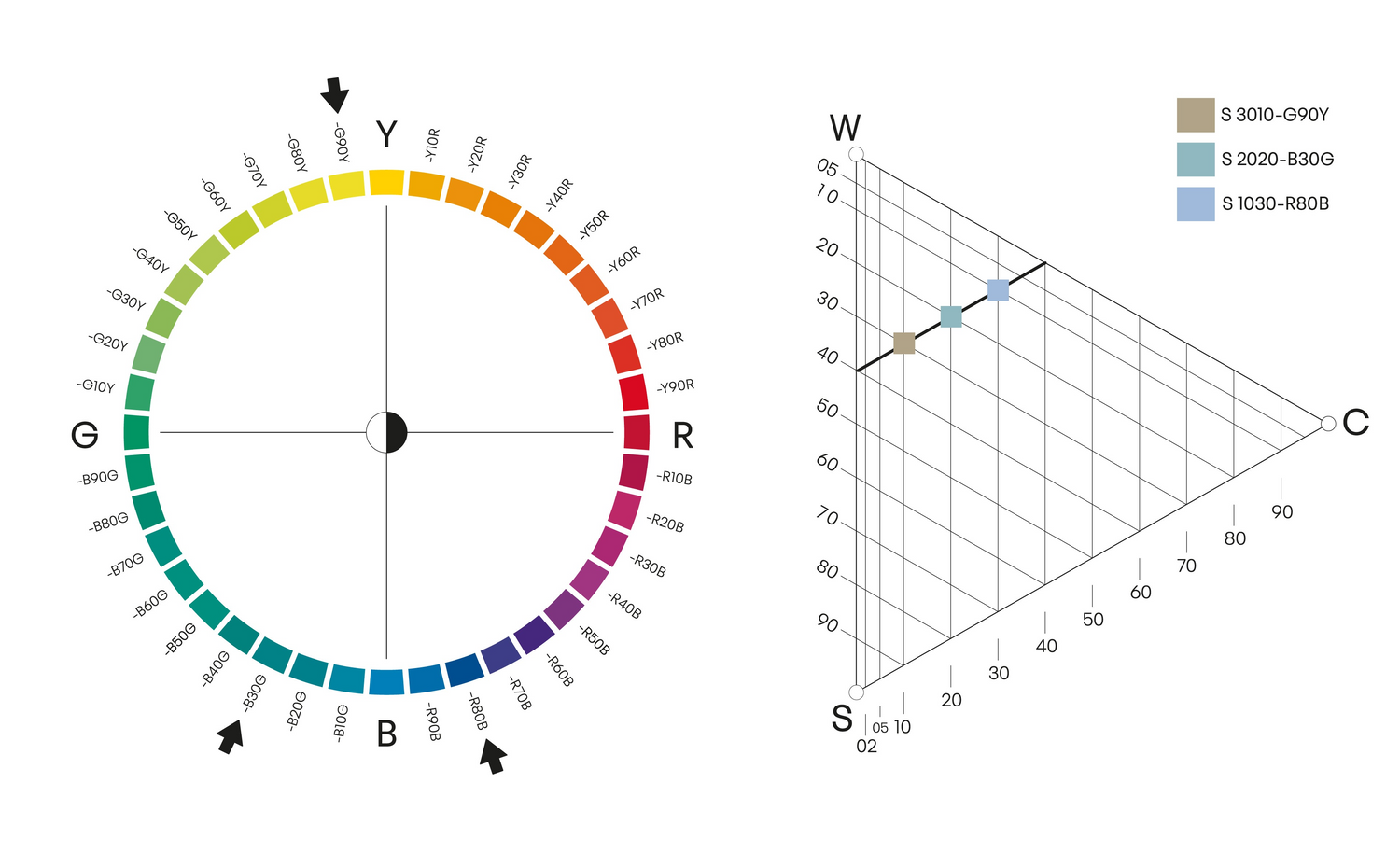
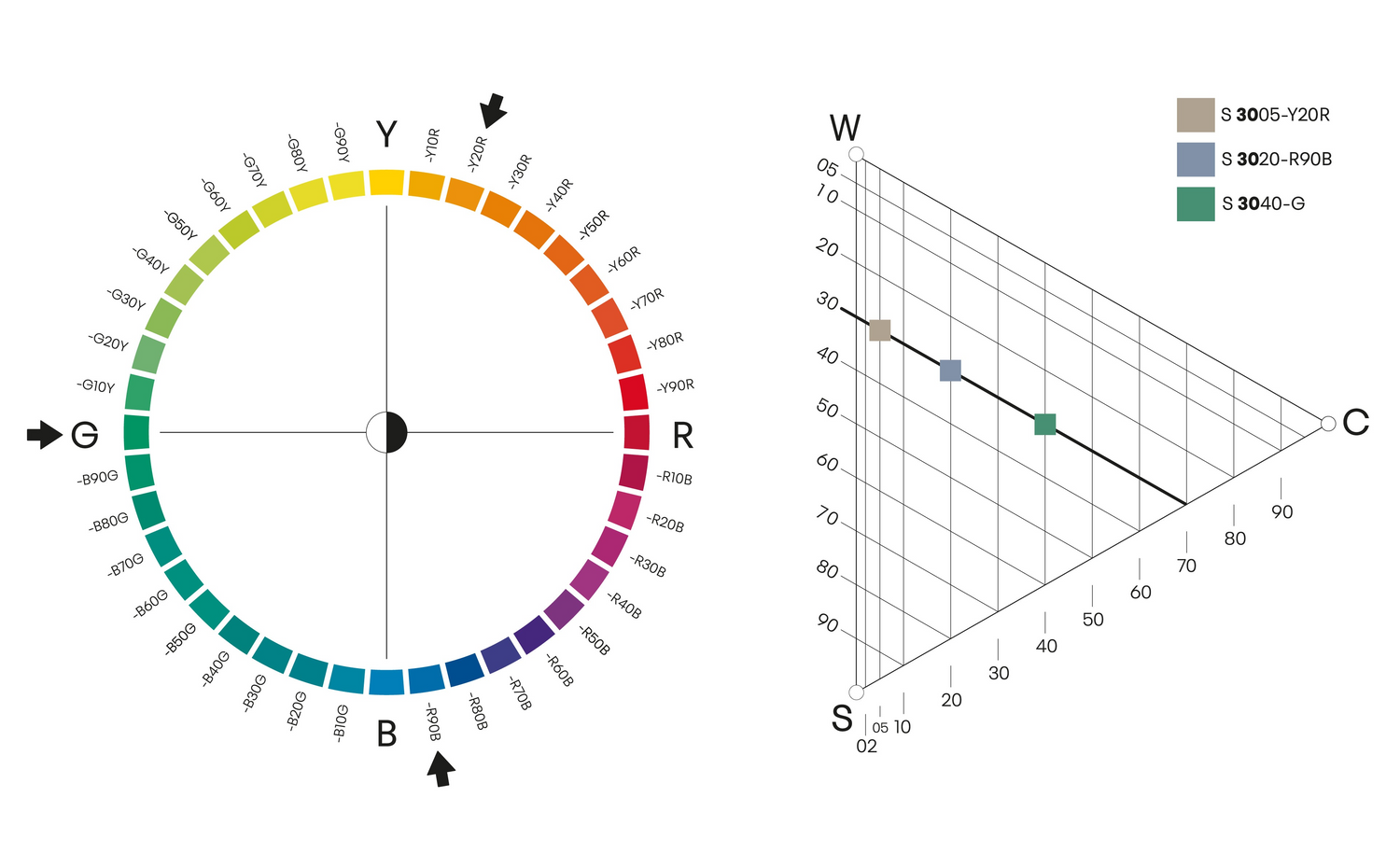
Vithet
Färgprover som har samma vithet finns på en rak linje parallellt med skalan mellan svart (S) och den maximala färgen (C). Ju mindre vitaktig färgen är, desto närmare ligger den denna skala. Vithet är användbart i mönsterskapande.
Vitheten beräknas på följande sätt: 100 % - (S + C) = vithet%.
Här är det illustrerat med tre olika färger med samma vithet (60). Till exempel, vitheten i nyansen 3010 beräknas som 30 + 10 = 40, 100 - 40 = 60, så vitheten är 60.
NCS egenskaper
Färglikheter
NCS systemet ger möjlighet att experimentera med andra färgegenskaper också. Likheterna i kulörton, nyans, kromatiskhet, svarthet och vithet är NCS grundläggande egenskaper och finns naturligt i NCS systemet. Dock kan andra färglikheter, såsom mättnadslikhet, ljushetslikhet och komplementfärger, definieras av NCS systemet trots att de inte är grundläggande egenskaper.
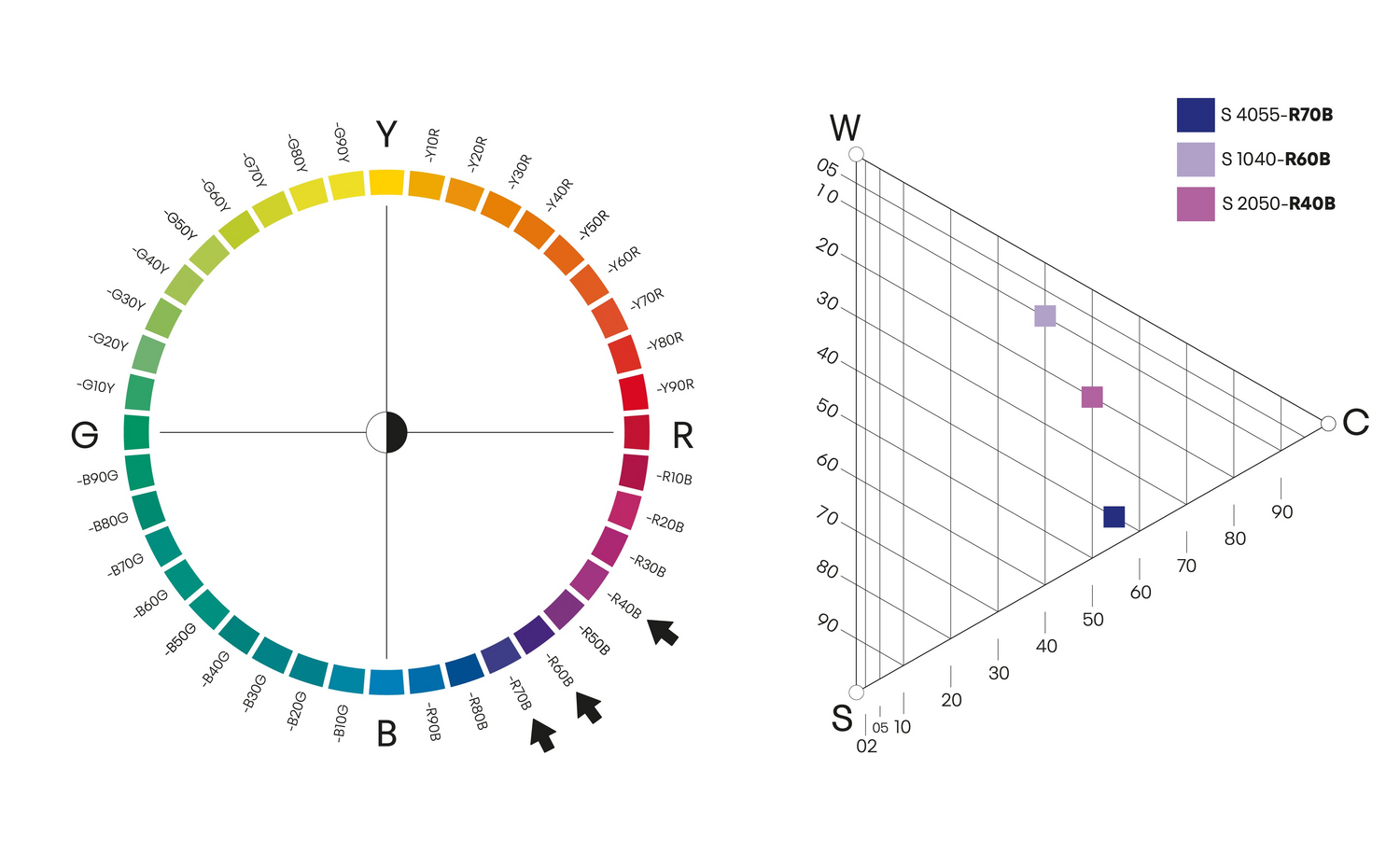
Närbesläktade färger
Närbesläktade färger är färger som ligger inom tio steg från varandra på färgcirkeln. De kan vara var som helst på cirkeln, men de måste ha ett maximalt avstånd på tio steg. Här är det illustrerat med tre olika kulörtoner: S 4055-R70B, S 1040-R60B och S 2050-R40B. Dessa färger är också olika nyanser, vilket gör dem mer intressanta.
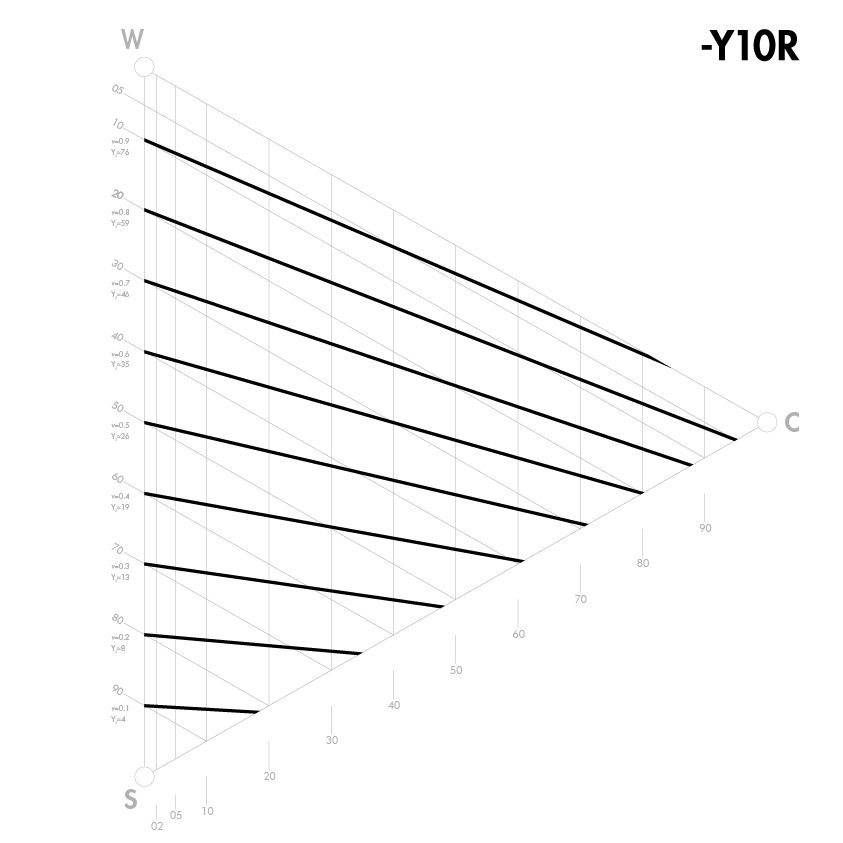
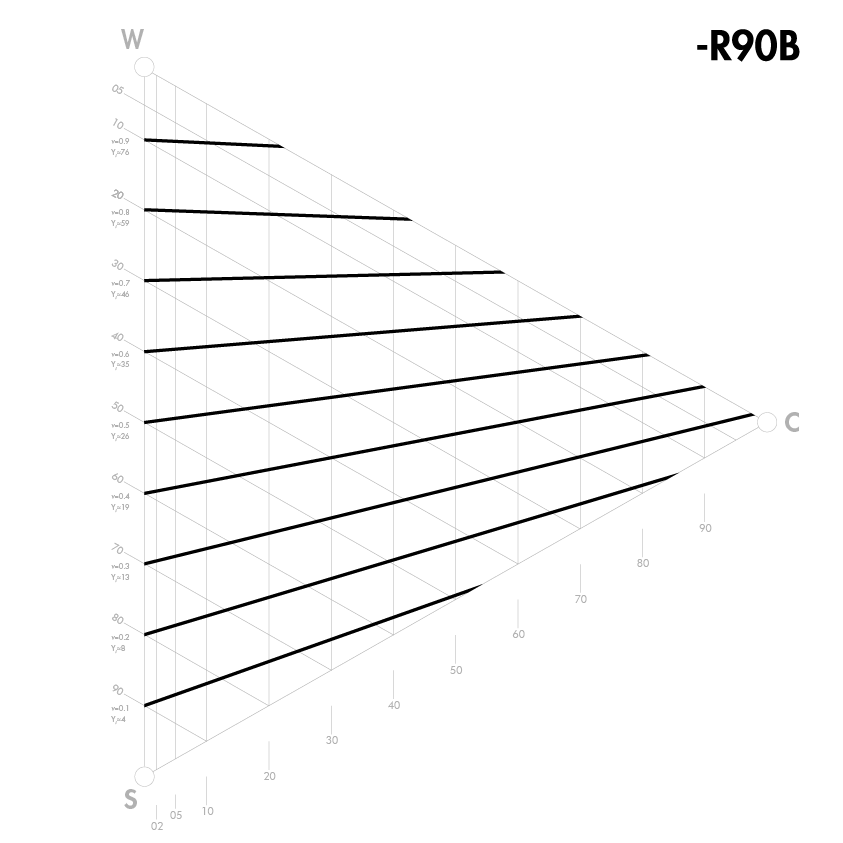
Färger med samma ljushet
En skillnad i ljushet mellan två färger är troligen den viktigaste faktorn i den visuella upplevelsen av ett mönster eller en form. Ljushet visar hur två färger kontrasterar mot varandra. Det är också avgörande för design och färgscheman för både utomhus- och inomhusmiljöer, särskilt för personer med nedsatt syn (t.ex. äldre), som behöver kontrast i ljushet mellan olika ytor för att kunna orientera sig.
Ljushet är inte samma sak som vithet. Vithet och svarthet är grundläggande egenskaper på samma sätt som gulhet, rödhet, blåhet och grönhet är, då de karakteriserar en färg. Ljushet är inte en grundläggande egenskap, men den kan bestämmas genom att jämföra färger via gråskala eller genom instrumentell mätning. En gul färg har en inneboende ljushet, medan en blå färg har en inneboende mörkhet.
Eftersom ljushet inte är en grundläggande egenskap, beskrivs den inte av NCS-notation och indikeras inte direkt av NCS-symboler. I NCS-Atlas anges färger som är lika i ljushet med linjer i varje färgtriangel. NCS-ljushetsvärdet indikeras med ett "v" i NCS Atlas på vänster sida av triangeln mellan W och S. Det finns även en ljushetsskala (NCS Lightness Meter) med 18 steg som är ett bra hjälpmedel för att bedöma ljusheten hos olika färger.